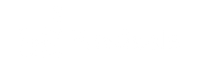A north star metric (NSM) is a single, critical measurement that reflects the long-term value a company provides to its customers. It effectively represents your product’s success and captures the essence of the core value your product delivers.
By focusing on this singular metric, teams can align their strategies and actions, fostering a culture of accountability and driving collaboration across departments.
This alignment ensures that every team member, from marketing to product development, is working towards the same goal. This leads to enhanced customer value, sustained growth, and a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Importance of NSM
NSM provides a vital strategic focus for businesses and helps steer decisions at every level. Here are the key reasons why having a clear NSM is so critical to your business:
1. Focus
A defined NSM helps your teams prioritize their efforts and allocate resources where they matter the most. By concentrating on a single, critical measure, teams avoid distractions and focus on delivering the most impact.
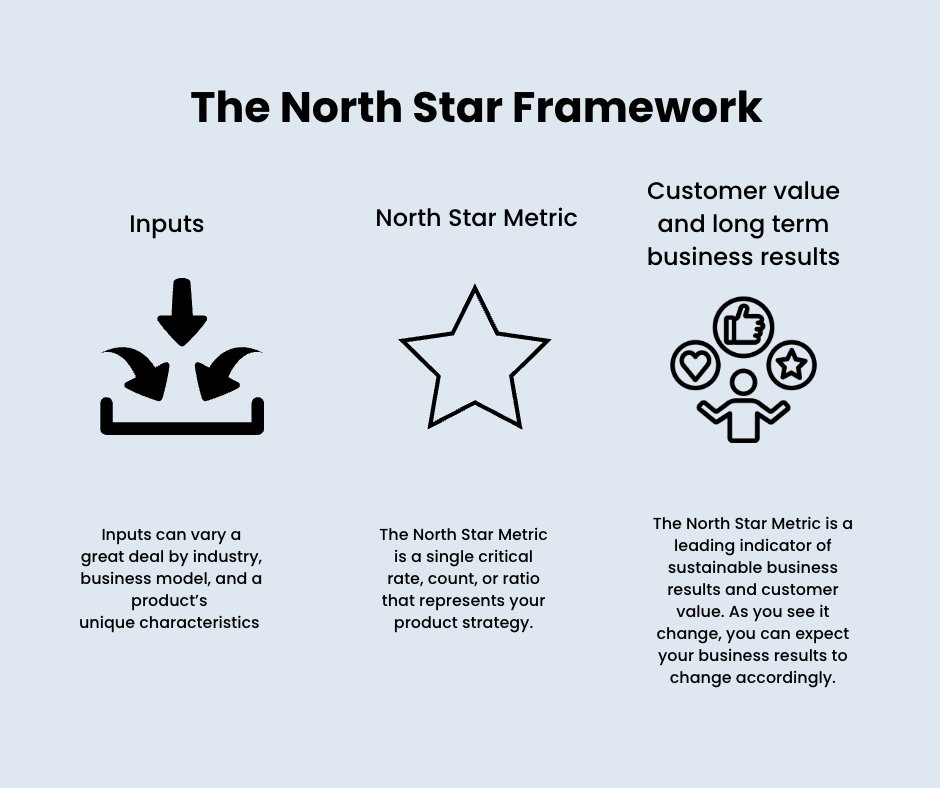
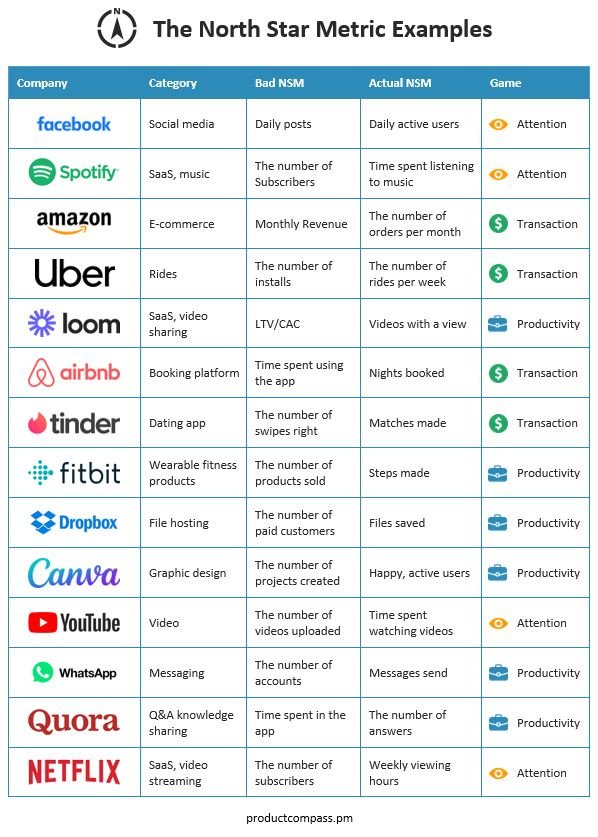
For example, Netflix identifies its NSM as time spent watching content per user. With this focus, Netflix prioritizes initiatives like improving content recommendations and optimizing user experience, rather than getting sidetracked by other secondary metrics like app downloads.
2. Alignment
The NSM ensures that all departments and teams are working towards a unified goal. This shared objective fosters collaboration and prevents the isolating of efforts that can detract from overall company growth.
For example, a SaaS company might define its NSM as the number of active monthly users. All departments like product, marketing, and customer success should work toward increasing this metric. Product teams would focus on user-friendly features, while marketing teams will create campaigns to onboard more users, and customer success will ensure users remain engaged.
3. Simplicity
Businesses often drown in a sea of metrics, but an NSM simplifies your approach. By boiling down success to a single metric, it becomes easier for everyone, from executives to entry-level employees, to understand what’s driving the company’s growth.
4. Long-term vision
While many metrics focus on short-term performance, the north star metric encourages a more sustainable and forward-looking approach. It aligns the company’s efforts with long-term growth by continually improving the core value your product offers to customers.
For example, Duolingo’s NSM is the number of badges acquired by language learners, encouraging the company to focus on user retention and learning outcomes rather than just sign-ups.
A comparative overview: NSM vs KPIs vs OMTM
Businesses often have multiple metrics to track performance, but it’s important to distinguish between different types of measures, each serving unique roles:
| Aspect | North Star Metric (NSM) | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | One Metric That Matters (OMTM) |
| Definition | The single most important metric that captures your product’s core value. | A set of quantifiable measures used to track specific business goals or performance. | A metric that the company focuses on for a specific period, often based on immediate priorities. |
| Scope | Broad and long-term, covering the entire business and its growth strategy. | Department-specific or project-specific, often focusing on specific areas of performance. | Narrow focus on a single, high-priority metric at a time, which may change based on shifting business needs. |
| Purpose | Aligns the whole organization towards delivering long-term value to customers. | Monitors various aspects of business performance, helping track progress towards goals. | Highlights the most important metric to focus on right now for tactical improvements. |
| Focus | Value delivered to customers that drives overall business growth. | Tracking and improving performance in specific areas such as sales, marketing, customer support, etc. | A temporary metric that may relate to a specific initiative, experiment, or stage of growth. |
| Organizational Impact | Aligns the entire organization around a single goal. | Helps teams and departments measure and manage their performance. | Focuses the entire company on solving one critical issue or seizing one key opportunity. |
| Examples | Slack: Number of daily messages exchanged between team members. | Slack: Daily Active Users (DAUs), Average Time Spent in Channels, Channel Engagement Rate, User Retention Rate | Slack: Weekly Active Users who send at least five messages a day. |
For effective integration, NSM, KPIs, and OMTM must work in harmony. The NSM sets the overarching goal, giving the organization a clear direction.
KPIs then break this down into actionable, department-specific metrics that contribute to the NSM, ensuring every team’s performance is aligned with the long-term objective.
The OMTM provides immediate focus on short-term priorities, acting as a tactical lever to accelerate progress on key KPIs, which in turn, push the NSM forward.
Common NSMs across industries
Below are some common NSMs across different industries:
1. eCommerce: Gross Merchandise Value (GMV)
Why it works: Reflects the total value of goods sold and the platform’s ability to generate revenue from transactions.
2. SaaS: Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
Why it works: Shows the consistency and growth of subscription-based revenue, a crucial indicator of business health.
3. Media: Daily Active Users (DAUs)
Why it works: Measures engagement, which drives ad revenue and content consumption.
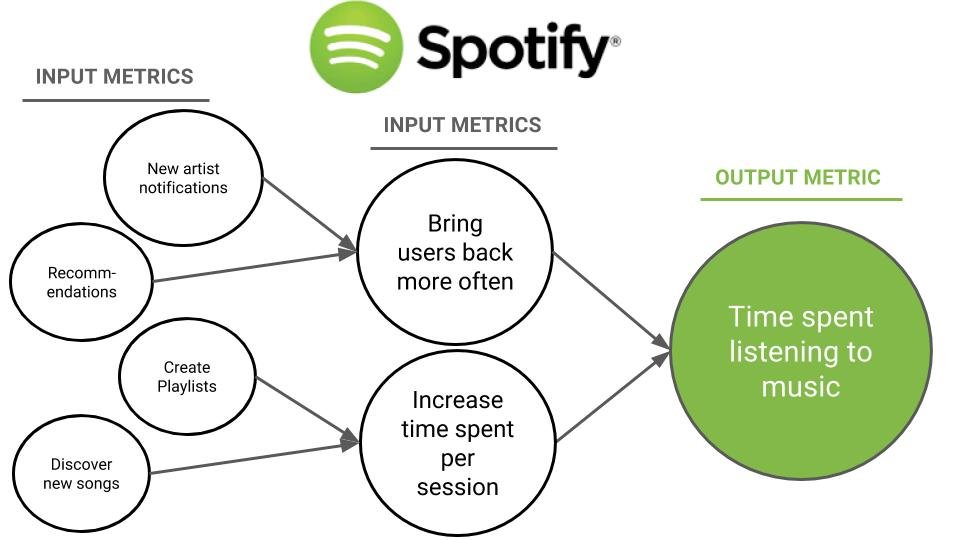
For instance, Spotify’s north star metric is time spent listening per user, a critical indicator of engagement.
4. Fintech: Total Payment Volume (TPV)
Why it works: Indicates the overall volume of financial transactions handled, a direct measure of growth and customer trust.
5. Healthcare Tech: Number of appointments booked
Why it works: Tracks how well the platform connects users with healthcare providers, a core value proposition.
6. Education Tech (EdTech): Course completion rate
Why it works: Reflects the effectiveness of the platform in engaging users and delivering educational outcomes.
7. Travel: Bookings made or trips taken
Why it works: Captures the platform’s core activity of travel bookings by user, indicating customer value and business growth.
How NSM guides A/B testing and Experimentation
The NSM plays a crucial role by providing direction and focus. By linking experimentation efforts to the north star metric, businesses can prioritize tests that have the most potential to impact this key performance indicator (KPI), driving meaningful growth and customer value.
1. Prioritizing high-impact experiments
When A/B tests are designed, there are often dozens or even hundreds of potential ideas to explore. By ensuring that experiments align with the NSM, businesses can focus on initiatives that directly contribute to their core value proposition.
For example, if a company’s NSM is monthly active users (MAUs), experiments that improve user engagement, reduce churn, or enhance the onboarding experience would take precedence over those that don’t have a direct impact on active user growth.
2. Maintaining focus across experimentation efforts
Experimentation can often become fragmented, with teams testing various elements of the product or user experience. When all experiments are aligned with the NSM, there’s a unified direction across departments.
This avoids scattered efforts and ensures that every test has a clear objective: to improve the metric that drives the core value of the business.
For example, if the NSM for a SaaS company is product usage depth, resources can be focused on running A/B tests related to feature improvements, user flows, or interface design to drive this metric.
3. Measuring the long-term impact of experiments
While some A/B tests deliver immediate results in terms of short-term metrics, the north star metric ensures that experiments are evaluated based on their long-term impact.
Instead of focusing solely on quick wins, businesses can use the NSM as a benchmark to measure whether experiments lead to sustainable growth and improvements in customer value over time.
Consider an eCommerce platform that might run an A/B test to improve checkout completion rates. While a test might boost short-term conversions, it’s important to also evaluate whether this change positively impacts the NSM, such as customer lifetime value (CLV), in the long run.
Explore A/B testing with a free 30-day trial!
Actionable next steps for your business
1. Assess your current metrics and their alignment with your core value proposition
Start by reviewing the metrics you’re currently tracking. Ensure they reflect the true value your product delivers to users and how closely they align with long-term business goals.
2. Engage stakeholders in discussions about potential north star metrics
Involve key stakeholders from all relevant departments – marketing, product, engineering, and customer success in a collaborative discussion about which metrics best capture your product’s value.
3. Choose a metric and implement tracking systems
Select the most relevant and impactful metric. Set up the necessary tracking systems and ensure your analytics tools can measure and report on this metric effectively.
4. Align teams and processes around your new NSM
Communicate the importance of the NSM across teams. Ensure everyone understands how their work contributes to improving the NSM and ultimately, the company’s growth.
5. Regularly review and refine your approach
Continuously monitor how well the NSM reflects the company’s goals and customer value. Be prepared to adjust or evolve the NSM if business needs or customer behavior changes.
6. Ensure continuous feedback loops for improvement
Create feedback mechanisms within teams to identify opportunities for improvement. Use these insights to make data-driven decisions that enhance the customer experience and drive the NSM forward.
Ready to find your north star metric?
Now that you have a roadmap to choosing, implementing, and refining your north star metric, it’s time to take action.
Start by assessing your product’s value proposition, involve your stakeholders, and set your business on a course to drive meaningful growth through your NSM. Make the commitment to focus on what truly matters and transform your approach to long-term success.