What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a graphic representation of the path that customers take when they connect with your brand through all touchpoints and channels (social media, live chat, email, etc.). It makes sure that no client is overlooked while promoting.
Business executives can also use this method to understand typical customer problems, which will enable them to improve and customize the user experience.
Although a customer journey map can take many various forms, it typically consists of an infographic. The objective is always the same – to help businesses understand their customers better.
What is customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping, also known as user journey mapping, is the method of producing a customer journey map, a visual narrative of your consumers’ experiences with your company. This exercise enables firms to examine their operations from their clients’ viewpoints by putting themselves in their client’s shoes. It helps in understanding common client frustrations and how to address them.
What is the purpose of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool, with the primary objective to enhance the customer experience and to guide the customer’s interaction with your product or service by providing what they need at every step of their journey.
Importance & benefits of customer journey mapping
Consumer journey mapping is significant since it is a tactical strategy for better recognizing customer expectations and is essential for enhancing the customer experience.
Customer expectations are changing for all businesses irrespective of their size – customers now expect an omnichannel approach for marketing, sales, and customer care.
Numerous advantages of customer journey mapping include:
- Identifying possibilities to improve the customer onboarding process as the map shows the customer’s journey as they move through the sales funnel.
- Comparing the client experience your customers expect with what they get. This encourages an effective engagement between businesses and customers.
- Recognizing how the various buyer personas differ as they transition from prospect to conversion across the purchasing funnel.
- Creating a logical sequence for your buyer’s experience helps in enhancing the content marketing strategy based on customer experiences.
- Enabling SMEs to develop customized experiences for each individual across all interactions and platforms.
- Placing the user at the forefront of the organization’s strategy. It demonstrates how customer behaviour has changed due to the web, social media, and smartphones. It shows how the entire business must adapt and adjust.
- Inspiring team members throughout the company to take the user’s wants, concerns, and feelings into account.
The biggest advantage, though, is just understanding your customer better. You can effectively personalize the customer experience to their demands if you have a better understanding of their expectations.
Steps to create an effective customer journey map
Follow the below steps to create an effective and efficient customer journey map:
Step 1: Set clear objectives for the map
Before you begin building your map, setting a clear goal is crucial because, without one, it will be challenging to assess whether the customer journey map will have a real influence on both your clients and your company. Ask yourself the:
- Why? – The Motive
- What? – Aim you want to achieve
- Who? – Your target
Step 2: Research your user personas and understand their goals
Creating buyer personas is a crucial first step in figuring out who your ideal consumers are. The persona on which your customer journey map will be based should have as much detail as feasible.
The most valuable and relevant information you can gather comes from real consumers – those who have interacted with your business or potential customers— who are genuinely interested in its goods and services. Obtain useful client information using any of the following methods:
- The feedback can be gathered through questionnaires, surveys, interviews, etc.
- User testing
- Customer service specialists who communicate with clients regularly
Some questions that can be asked are:
- How do customers discover or come to know about your brand?
- If/when/how customers buy, return, or cancel.
- User experience while using your website.
- Your brand’s ability to solve problems (quality of customer support).
As soon as you are clear on the many client personas and how they interact with your business, it is best to concentrate your attention on only one or two of them because grouping too many personas in one journey won’t fairly represent your customers’ experiences in the map.
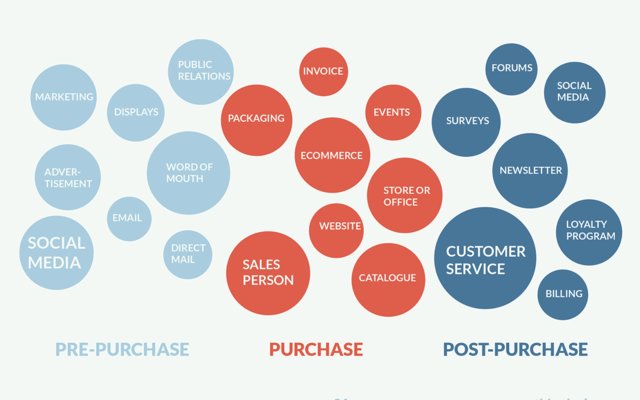
Step 3: Define and list all the touchpoints
‘Touchpoints’ are interactions between a customer and the brand before, during, or after a transaction takes place. This includes offline and online engagements, marketing efforts, in-person interactions, and phone conversations.
It’s important to consider every possible point of contact that can exist between your customers and your business. By doing this, you’ll ensure that you don’t miss any chances to pay attention to your client’s needs and make adjustments that will satisfy them.
Step 4: Determine the existing and the required resources
Nearly every aspect of your organization will be covered by your customer journey map. The resources used to create the customer experience will be highlighted by this. Therefore, it’s crucial to evaluate the resources you now have and those you’ll require to enhance the customer experience.
You can effectively forecast how new resources and tools will affect your company and generate outsized value by integrating them into your map. As a result, persuading key decision-makers to support your plans is a lot simpler.
Step 5: Analyze the results by taking the customer journey yourself
Until you attempt it, the entire customer journey planning exercise is just a theoretical exercise.
Follow the path that each of your personas takes by monitoring their social media posts, emails, and online searches. Analyzing the outcomes will help you to identify areas where consumer needs are not being satisfied. By taking this approach, you can make sure you are offering a worthwhile experience and demonstrating that users can discover a resolution to their issues with the expertise and support of your business.
Step 6: Make the required improvements
Your data analysis should help you determine exactly what sort of website you want. Then, you can modify your website to efficiently accomplish these objectives, no matter how big or tiny the adjustments are. As they are directly tied to the problems that customers identified, experimenting and testing improvements like creating more distinct call-to-action links or writing longer descriptions under each product can make them effective.
Best customer journey mapping tools
Customer journey mapping tools are software that gathers and display both quantitative and qualitative information on how customers engage with your website or product, helping you to better understand your target market. They provide you with information about your visitors’ origins (offline/online), and their online behaviour, and capture direct user feedback. You need additional data to map out a sophisticated consumer journey. Your data from various customer touchpoints and channels can be obtained with the correct combination of customer journey mapping (CJM) solutions. There are three types of mapping tools that help create better user experiences based on the part of the journey a customer is in:
- Analytics tools
- For websites: These tools provide quantitative statistics on traffic and demographic parameters like bounces and bounce rate, new and returning users, and goal conversion rates
- For user behaviour: These provide qualitative insights about user interaction and behaviour (time spent, buttons clicked, exit) with the website.
- Examples: Google Analytics, Heap, VWO Insights
- Customer journey map visualization tools
Traditional customer journey mapping solutions are flowchart builders, which are essentially digital copies of sticky notes that can be shared with your team and transformed into a collaborative environment that is favourable to remote work.
Examples: A Whiteboard, Powerpoint, Smaply, LucidChart
- User feedback tools
With the aid of voice of the customer (VoC) solutions, you may discover in their own words what your customers feel and believe about your company and products. Having everything in one place makes it easier to gather unfiltered, genuine feedback about how others view you at every step of the journey.
Examples: Simplify, Clarabridge, InMoment
Take into account that your client journey map is a dynamic, ever-evolving document. It should continuously evolve along with your ever Changing and developing customers. Test, revise, and enhance your customer journey plan at least once every six months. Every time you make substantial modifications to your product or service, customer journey maps should also be adjusted appropriately.