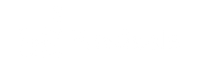What is a content hub
A content hub can be defined as a centralized repository with a collection of pages that provide information related to a common topic. The pages are interlinked and offer a broad overview of the main topic as well as deeper insight into the subtopics.
Key elements of a content hub
A content hub consists of 3 main parts:
- Pillar page: Also known as hub page, it is typically a high-level guide that acts as an introduction to a particular topic. It provides a good starting point for additional information on the topic.
- Spoke content: In-depth guides such as blogs and long-form articles make up subpages of content focused on specific aspects of a topic.
- Internal hyperlinks: The hub page and subpages are interconnected with internal hyperlinks so that users can navigate the topic until they’ve exhausted all the information and gained all the knowledge they need.
The below image represents the structure of a content hub:

Various platforms as content hubs
Some of the common platforms used as content hubs for various marketing efforts can be classified as below:
- Digital Asset Management (DAM): These are software tools that allow businesses to manage, distribute, collaborate, and secure digital assets. Permission controls, rights management, and asset performance analytics are among the features of DAM platforms. Some examples of digital assets are:
- Images
- Videos
- Word documents
- PDFs
- Graphics
- Design files
- Content Marketing Platform (CMP): Using this solution, content marketing teams can plan, imagine, collaborate, and create materials to increase brand awareness, improve lead generation, and increase revenue.
- Product Content Management (PCM): It is a merchandising discipline that incorporates aspects of retail merchandising, digital marketing, and content strategy into one. This is beneficial for maintaining product information in product-oriented, SKU-heavy businesses.
- Marketing Resource Management (MRM): The objective of this marketing technique is to help businesses combine their resources – procedures, operations, content, workflows, and data – into a single system to support their marketing campaigns and programs.
Types of the content hub & examples
- Classic hub & spoke
Format: A parent page along with multiple (5-20) subpages.
This type of content hub model is best for evergreen kind of content which doesn’t require a lot of overhauls.
CoinTelegraph, a cryptocurrency news website that includes an education section, provides a good example of the hub and spoke format. Each major currency has its hub (e.g. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, etc.) that utilizes evergreen content.
- The content library
Format: In this format, content is sorted by category or subgroup, with links to the corresponding category subpages.
A content library is probably the best format for your readers if your content is spread across many categories (such as blogs or media publications).
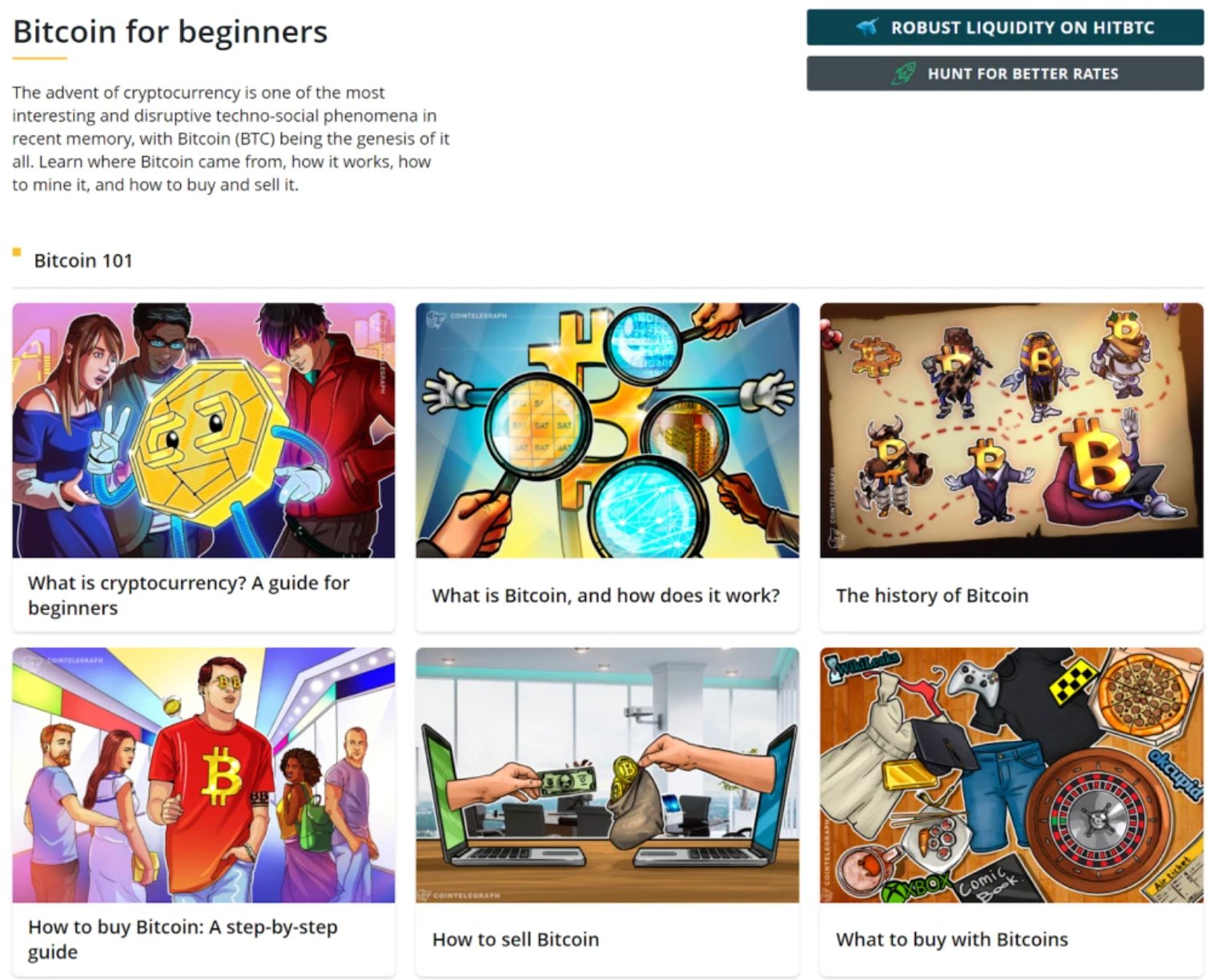
A good example of this model is, HelpScout’s resources & guides providing category-wise posts on their hub page.
- The topic gateway
Format: An overview of the topic is presented, along with links to evergreen resources, with a list of the most recent publications for that topic at the end of the page.
This format is particularly useful if you have a lot of content on a particular topic. Beginners can easily explore your evergreen resources, while those with more experience can easily find more recent content.
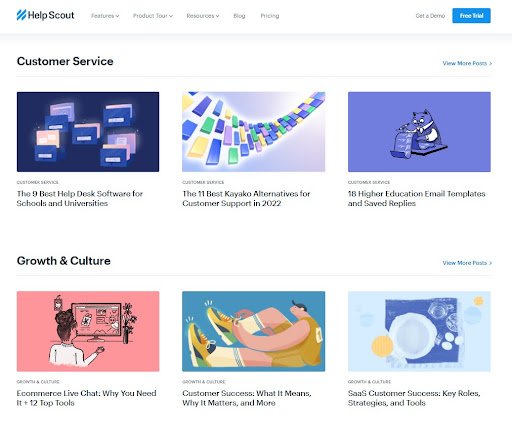
DietDoctor’s “Keto for Beginners” guide is an excellent example of this format. It is a static landing page filled with everything someone researching a ketogenic diet may want to know.
- The content-database
Format: Hundreds, perhaps thousands, of child pages, all sortable and filterable by taxonomy.
This format works much like a glossary or directory, so users can quickly sort through large amounts of similar content to find precisely what they are looking for.
As an example, Audubon’s “Guide to North American Birds” hub page links to articles about each bird.

- The topic matrix
Format: Multiple consistent subpages of content indexed specifically.
This type of content is most relevant for the informational type content such as on medical sites where clear navigation and access to information are of utmost priority.
As an example, this type of format can be seen on the Mayo Clinic’s disease & conditions hub.
Importance of the content hub
A content hub is worth the effort to build brand awareness, brand loyalty, and organic search ranking. With long-form content aimed at solving your audience’s problems, you’ll build credibility and brand loyalty.
Some of the benefits of having a well-structured content hub are:
- Increase in topical authority
Google and other search engines will rank your content higher in SERPs for relevant keywords if they recognize you as a trusted source. Here’s how content hubs help:
- As a content hub provides extensive material about a topic and subtopics, it is a signal for Google for your expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
- It increases the off-page SEO factors such as backlinks, social signals, and brand mentions from trusted sources, resulting in higher rankings.
- Better audience engagement
By providing exhaustive resources on topics, content hubs inspire engagement in the form of:
- Staying longer on the pages
- Clicking on multiple links
- Reduced bounce offs
- Increased repeat visits
These are reassurances to search engines about the quality and usefulness of content.
- Lead generation
A content hub allows you to generate more leads by providing valuable and relevant information to users. High-quality content displays your expertise and will effectively attract and nurture prospects from the first visit itself.
- Valuable marketing insights
Tools like Google Analytics can provide you with detailed analytic reports on the content hubs. These metrics help the content creation team understand what excites the users and what doesn’t. Hence, enabling the publishing of more effective content.
How to create a content hub
The below infographic summarizes the important steps to creating a content hub. Read here for more detailed information.

Creating a content hub and regularly updating it with blogs along with curated, user-created, or collaborative content can keep you ahead in the race. In the end, whichever model you choose to share your expertise with customers, a well-organized content hub will help you dominate the Google space.