What is a canonical URL?
According to Google, a canonical URL is the preferred version or the best representative of a web page amongst a group of duplicate pages. It appears as a small code (also known as a canonical tag) on the page that tells search engines how to crawl the page and rank the importance of the content.
In other words, a canonical URL is a technical solution for duplicate content or pages.
Let’s take a look at the example of duplicate pages below:
- https://www.website.com/category/product-a/
- https://www.website.com/product-a/
- https://website.com/product-a/
- http://www.website.com/product-a/
- http://website.com/product-a/
- https://m.website.com/product-a/
- https://www.website.com/product-a
- https://www.website.com/product-A/
To a user, all the above URLs display the same content. However, to any search engine, there are eight duplicate pages. Many websites may have these kinds of duplicate issues, this is where canonical URLs help search engines to show the most relevant page result to the user.
What is a canonical tag?
The first canonical tag was introduced in 2009, with the main aim to help webmasters overcome duplicate or vastly-similar content that is accessible on multiple URLs.It is an HTML link element, with the attribute of rel=”canonical” and is found in the <head> element of a webpage.
Importance of Rel=Canonical for SEO
Search engines can easily get confused with the multiple duplicate contents available. The rel=canonical tag simplifies this and helps search engines to:
- Recognize the original version of the content
- Not ignore the page
- Rank the page appropriately
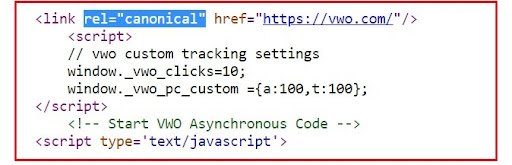
How to spot a canonical URL
The canonical URL for a webpage can be seen in the source of that page. This element is only visible to the search engines and not to the users. Below is an example:
Importance of canonical URLs
Canonicalization helps in boosting SEO rankings of websites and webpages in the below manner:
- They specify which URL the users should see in search results. Applying canonicals can help keep things “clean.”
- Simplification of tracking metrics for a single product/topic – canonical URLs help keep things simple and standardized, specifically when it comes to reporting performance to clients.
- They consolidate link signals for similar or duplicate pages and manage combined content that helps in consolidating page ranking to the preferred URL.
SEO considerations for canonical URLs
Understanding the proper use of canonicalization and setting canonical URLs is vital for an SEO practitioner. A flawed application of the same can negatively impact a website’s performance.
Although in most cases rel=”canonical” is the recommended method of compiling duplicate content for search engines, below are a few other ways to be considered for canonicalization:
- 301 redirect: This is a status code that informs search engines of the creation of a permanent redirect from one URL to another.
- Set passive parameters in the Google Search Console: These parameters are usually used to track visits but don’t change any content on the web page. It indicates to Google not to consider such URLs.
- Location hashes: A “#” at the end of a URL points a search engine to a specific spot on a website or a webpage.
When to use a Canonical URL
Below are some instances where a canonical URL should be used to identify duplicate content to meet SEO best practices:
- While reposting any existing content
- Blog syndication
- While A/B testing different pages
- eCommerce websites with multiple hierarchies
- In case of any unintentional duplication of content
Read this article to understand more about the dos and don’ts of canonical URLs.