In the vast and ever-evolving realm of web development, even the smallest details can wield significant influence over user experience and business outcomes.
Let’s delve into the frequently underestimated but crucial concept of z-index. Much like the unseen force guiding the arrangement of papers on a desk, the z-index determines the stacking order of elements on a webpage, profoundly shaping how users interact with digital content.
From engaging eCommerce platforms to sleek corporate websites, mastering z-index is a fundamental skill for businesses striving to leave a lasting impression in the digital landscape.
Definition
Z-index is a CSS property that controls how items are stacked on a webpage. Each element has a default stacking order based on its position in the HTML document, but the z-index property allows developers to control which elements appear in front of or behind others.
In web design, z-index plays a crucial role in managing the visual hierarchy of elements. It allows designers to control the layering of elements, ensuring that important content is prominently displayed and easily accessible to users.
Below is an image showcasing the z-index layout for reference.
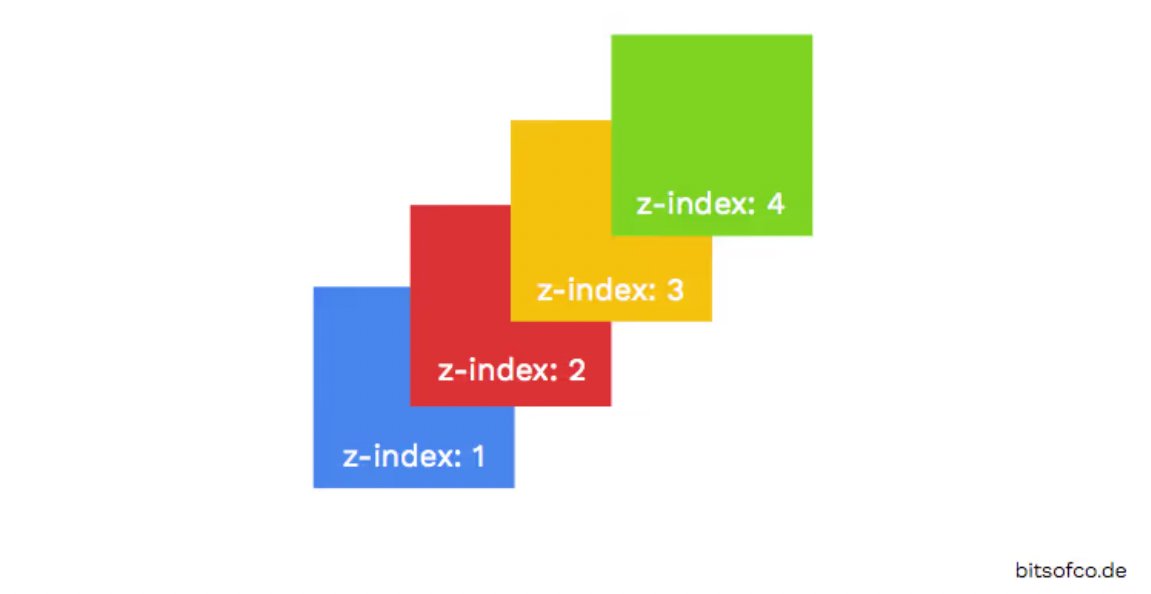
Importance of z-index
1. Enhancing user experience
Effective z-index management is essential for creating a seamless and intuitive user experience. By ensuring that elements are properly layered and organized, businesses can prevent visual clutter and confusion, making it easier for users to navigate and interact with the website.
For example, consider a news website where the headline article is placed above other news stories using a higher z-index value. This ensures that users immediately see the most important news when they visit the site.
2. Impact on conversion rates and sales
Z-index can have a significant impact on conversion rates and sales. By strategically placing important elements such as call-to-action buttons or product images above other content, businesses can draw attention to key actions and encourage users to take desired actions, such as making a purchase or subscribing to a newsletter.
For instance, an eCommerce website may use a prominent “Add to Cart” button with a higher z-index value, ensuring it stands out on the product page and encourages users to make a purchase.
3. Building brand perception and credibility
A well-designed website reflects positively on the professionalism and credibility of a business. Proper z-index management contributes to a visually appealing and user-friendly website, enhancing brand perception and fostering trust and loyalty among users.
For example, a clean and organized layout with well-organized content sections and prominent branding elements can leave a positive impression on visitors, increasing their confidence in the brand and its offerings.
Real-world examples of z-index
Let’s delve into real-world examples of z-index usage in web design, showcasing how z-index plays a pivotal role in enhancing user interaction and engagement.
1. Navigation menus
Many websites use fixed or sticky navigation menus that remain visible as users scroll down the page. By applying a higher z-index to the navigation menu, it stays on top of other content, ensuring easy access to essential navigation links at all times.
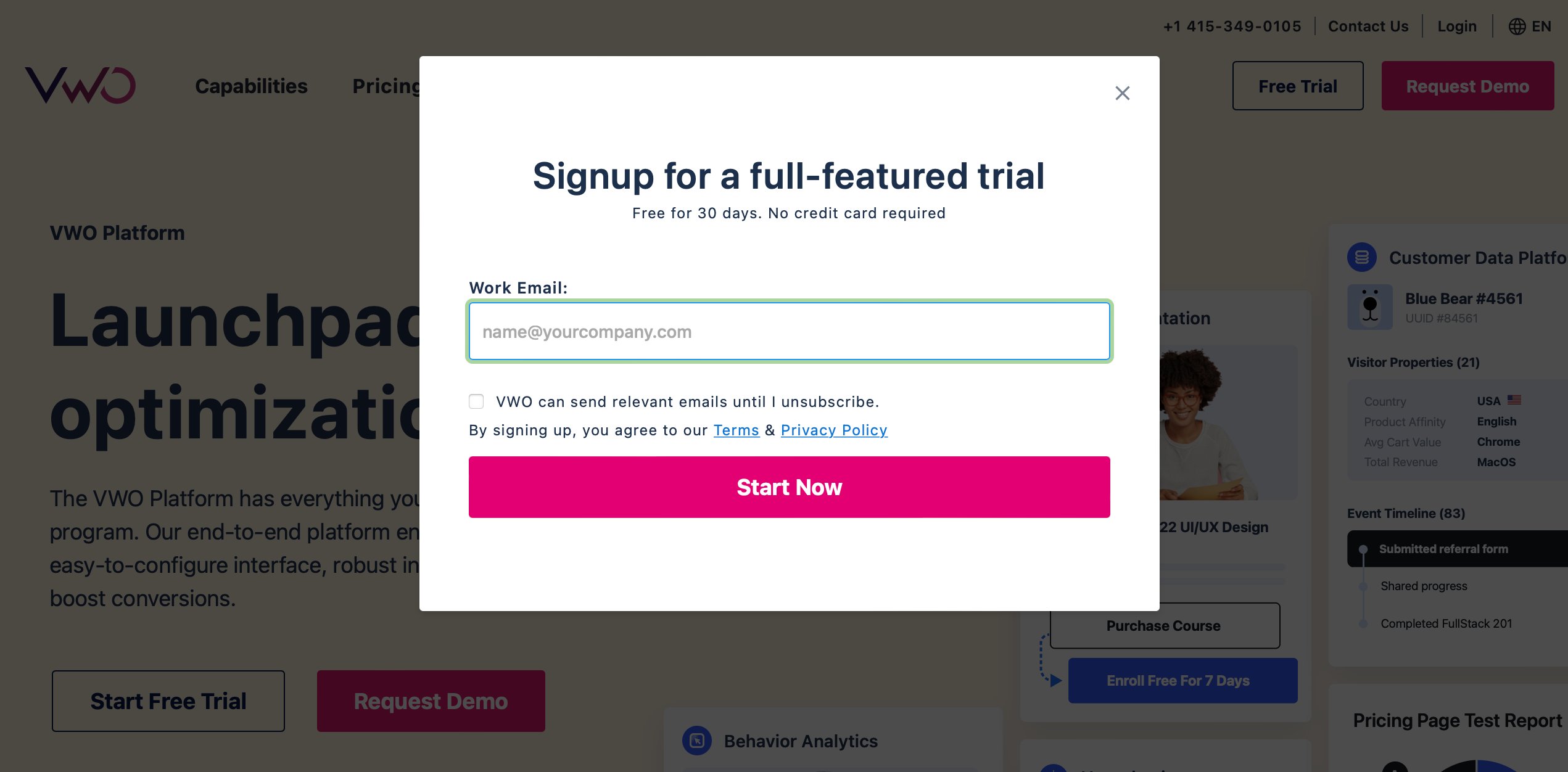
2. Pop-up modals
When a website displays pop-up modals for login forms, newsletter subscriptions, or promotional offers, a higher z-index ensures that the modal appears above the rest of the page content, grabbing the user’s attention and focusing their interaction on the modal.
3. Carousel sliders
Websites often feature images or content sliders to showcase multiple pieces of content within a limited space. By adjusting the z-index of each slide, designers can control the layering of content, ensuring that each slide appears in front of the previous one as users navigate through the carousel.
4. Overlay elements
Overlay elements like lightboxes or tooltips, which appear on top of existing content to provide additional information or functionality, rely on z-index to ensure they are visible and accessible. By setting a higher z-index, these overlay elements can effectively draw attention without obstructing other content.
5. Drop-down menus
Dropdown menus, commonly used in navigation bars or as part of form inputs, rely on z-index to ensure they appear above other page elements when activated. Proper z-index management ensures that dropdown menus are accessible and functional without being obscured by surrounding content.
Responsive design in top brand websites
Z-index is a fundamental aspect of web development used by businesses across various industries to manage the layering of elements on their websites.
Here are two examples of top brands utilizing z-index effectively:
Apple
Apple’s website is renowned for its sleek and intuitive design, which seamlessly adapts to different devices and screen sizes. Z-index is crucial for maintaining the visual hierarchy of elements on their pages, ensuring that important content such as product information, navigation menus, and calls to action remain prominent and accessible. Whether you’re browsing on a MacBook, iPhone, or iPad, Apple’s use of z-index ensures a consistent and user-friendly experience.
Nike
Nike’s website is another excellent example of effective z-index implementation in responsive design. As a global leader in sportswear, Nike prioritizes visual appeal and ease of navigation to showcase its extensive product lineup. Z-index is used strategically to layer elements such as product images, descriptions, and interactive features, allowing users to explore their offerings seamlessly across desktop and mobile devices. By carefully managing layering, Nike creates an engaging and immersive browsing experience that aligns with its brand image.
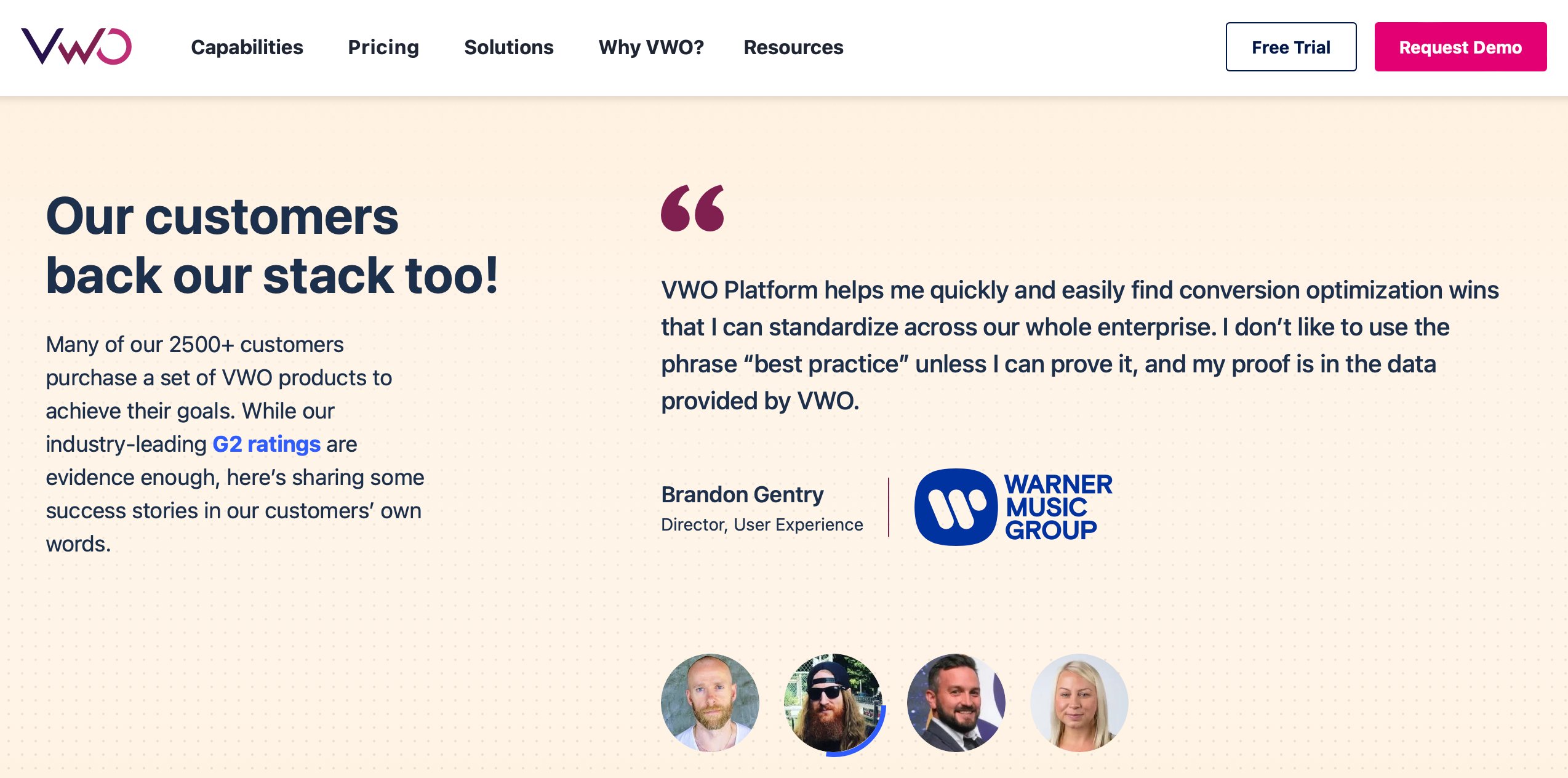
VWO
VWO’s website demonstrates a sophisticated utilization of z-index within its responsive design framework. VWO, a renowned provider of conversion optimization and A/B testing solutions understands the paramount importance of user experience in its digital presence.
Through meticulous z-index management, VWO adeptly organizes its website elements to ensure easy navigation and understanding for visitors on different devices, seamlessly integrating informative content sections and interactive tools.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of z-index is a critical component of web development, shaping the visual hierarchy and user experience on websites across various industries.
From enhancing navigation and user interaction to impacting conversion rates and brand perception, effective z-index management plays a pivotal role in creating engaging and user-friendly digital experiences.
As businesses strive to navigate the complexities of responsive design and dynamic layering, mastering z-index becomes increasingly essential. By leveraging adaptive techniques, such as media queries, CSS frameworks, and responsive layout strategies, designers can ensure consistent and intuitive layering across devices and screen sizes.