Many online businesses rely heavily on paid ads for development, thus it’s vital to track cost per click and maintain a positive ROI. CPC is a crucial factor for marketers to take into account since it quantifies the cost of a brand’s paid advertising efforts. The aim of marketers should be to lower click costs while still fostering high-quality clicks that will lead to happy consumers.
What is cost per click?
Cost per click (CPC) is a digital marketing statistic that establishes the price that advertisers must pay for the clicks that their advertisements receive when they are shown on websites or social media platforms like Facebook ads, Google ads, and others.
When deciding on bid strategies and conversion bid types to optimize clicks in proportion to the budget size and target keywords, CPC is a vital factor. It is a crucial bidding measure because if it is too high, you won’t be able to attain a return on your advertising spend (ROI).
Variables that influence the CPC
The cost per click is determined by the following variables, regardless of whether you advertise on Facebook, Google, or another platform:
- Maximum bid: The amount you’re prepared to spend if someone clicks on your advertisement.
- Quality Score: The quality score is based on several factors, including the quality of your landing pages, your click-through rate (CTR), and the relevance of your keywords.
- Ad rank: This is determined by both internal and external criteria, such as the searcher’s intent, the effectiveness of your ad during the auction, and the size of your bid.
Types of ads using CPC
CPC is a component in the calculation of overall paid advertising campaign expenditures for a range of text, rich-media, or social media campaigns. Some types of advertisements are exclusively seen on particular networks, such as the Google Search Network (ads at the top of Google’s search engine results pages) and the Display Network (Google-owned or partnered sites like YouTube and Gmail).
CPC affects several ad kinds, such as:
- Text advertisements
- Shopping advertisements
- Image ads
- Video ads
- Promoted tweets on Twitter
- Facebook ads
- Instagram ads
- LinkedIn ads
Calculate cost per click
The cost per click is calculated as the ad rank of the ad below you, divided by your quality score, plus one cent.

Since it is an average of bids made against many rival advertisers over some time, your cost per click as an advertiser will always be lower than or equal to your maximum bid. Your ad rank, maximum bid, and quality score, as well as those of your nearest rival, all have a significant impact on your real cost per click because of the way Google’s ad auction operates.
Definitions
Below are some good-to-know definitions of terms associated with cost per click:
Average cost per click
The average cost per click is simply the average amount an advertiser spends on each ad click and is calculated as below:
Average CPC = total cost of clicks / total number of clicks
Maximum cost per click
The maximum cost per click is what you are willing to spend and what you estimate a click to be worth. CPCs aren’t always paid at maximum rates. The real CPC will generally be less than that initial offer based on similar brands and quality ratings in search.
Manual cost per click
In contrast to automated bidding tactics, manual CPC bidding is when advertisers manually set the maximum CPC for each advertisement. In this kind of bidding, each brand selects its bid rates.
Enhanced cost per click
For specific ad kinds that show up on Google’s Search Network and Display Network, enhanced cost per click is an automatic conversion bidding approach in Google AdWords. To optimize ad conversions, enhanced CPC is applied.
Importance of Measuring Cost Per Click
CPC is essential in marketing and advertising since it helps advertisers:
- Become aware of the costs involved in obtaining ad clicks.
- Compare the results of their advertising activities against those of the competitors.
- Determine which advertising, ad groups, or ad campaigns produce the most return on investment.
- Reach objectives to increase traffic. Paying publishers to display advertising on websites where the target audience is likely to frequent will help you draw more clients to your sites or shops.
- Calculating CPC allows you to compare the price of sponsored advertising campaigns to the income they create or other criteria.
- Choose the appropriate ad formats. Change your budget to ad kinds that provide more money or visitors if you discover that CPC is not profitable for some ad types.
Lowering CPC While Maintaining Value
Every brand should strive to have a low CPC. Ads should thus be optimized for maximum value at a cheap cost. Since the main objective of CPC is to increase sales, it should also be comparable to brand profitability overall. Budgeting can be important because most firms don’t want to spend more on advertising than they make.
Hence, how can you reduce the cost per click while maintaining or perhaps increasing the quality of your visits? Therefore, the following courses of action ought to be taken:
Improve Quality Score
Putting your focus on the quality score when looking for ways to improve your campaign’s performance makes sense since it directly impacts your actual CPC.
Google has developed an automatic method that grants well-managed PPC advertisements with excellent quality scores and price breaks.
By following the below best practices for quality score, you may increase your chances of receiving a significantly lower cost per click:
- Improve CTR – The quality score is significantly affected by your CTR. An improved CTR shows that your result is one that searchers want to click on. It is done by:
- creating engaging, and relevant ads and CTAs.
- Include rewards and promotions
- High relevance of ads to the keywords
- Improve landing page – Landing pages that are relevant to your ad and keywords will help achieve a higher quality score than generic homepages. Implement the below tips to optimize your landing page:
- Keep the landing page content consistent with the ad message.
- Create and publish unique and captivating content
- Make it trustworthy by using reviews and testimonials
- Keyword Relevance – Keyword-relevant ads, which include the keywords in the text, tend to get higher click-through rates and quality scores.
- A/B testing your ad wording, various CTAs, headlines, and value propositions can help you achieve continuous performance improvement hence resulting in higher quality scores. Try VWO with an all-inclusive free trial!
Use negative keywords
Negative keywords might prevent your ads from appearing for irrelevant search terms and assist you in lowering and raising your CPC. They stop you from placing bids on irrelevant, competitive, or generic terms with abnormally low-quality scores.
Experiment with various ad positions
The CPC is determined by your competitor’s ad rank in the SERP position below you. By testing and comparing the effects of various ad locations on clicks and conversions, you may successfully lower your CPC.
Ad scheduling
There are other factors involved in bidding besides only keywords. By using ad scheduling, you can make sure that your ads are displayed at times of the day when your customers are most likely to be interested and convert. You may create a special ad schedule that helps you maintain and raise your average CPC while boosting conversions.
Implement device adjustments
You can alter your max CPC across mobile, tablet, and desktop devices in the same way that you can implement bid modifications depending on locations and the time of day. Identifying which hardware is supplying what data is crucial. For optimal CPC over devices, make sure you thoroughly analyze your data to determine audience actions.
Industry-wise average cost per click
The below infographics show the average cost per click for industries:
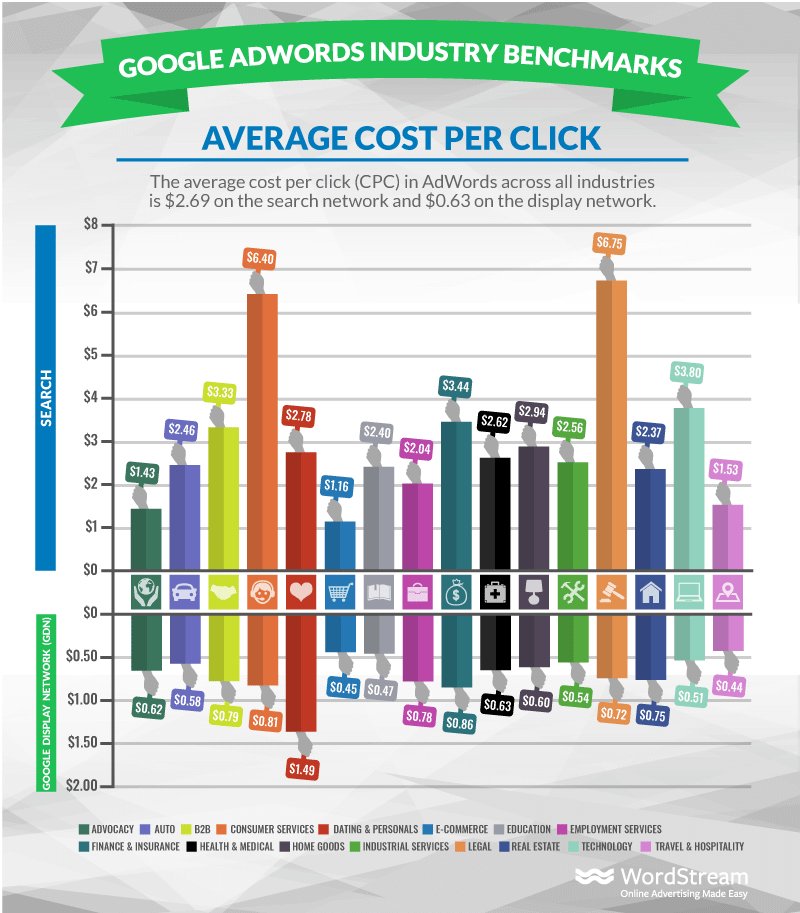
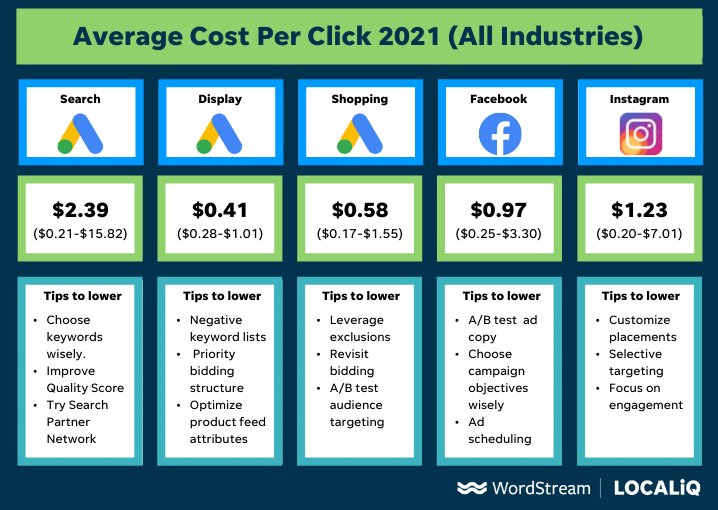
You will notice higher profitability and ROAS from your campaigns when you can successfully lower your cost per click without affecting visibility and clicks. There is no one way to achieve this, but by following the above procedures, you may keep making adjustments to better optimize your campaign and take pleasure in the outcomes!