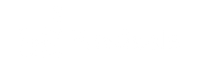What is churn rate?
Churn rate, also known as attrition rate, is a metric that refers to the percentage of customers who unsubscribe from a service and discontinue any kind of engagement with an entity over some time. It could mean that customers leave one business to go to the competitor.
For example, if a business has 100 customers and 5 of them leave, the churn rate is 5 per cent.
A high churn rate means more customers leaving the services. A low churn rate refers to the retention of more customers. For a business, having a lower churn rate is always beneficial.
Types of churn rate
Churn could be voluntary (active) or involuntary (inactive). Although both types result in loss of customers and revenue, they have different underlying causes and prevention strategies. Let’s look at the two types separately:
Voluntary churn
This kind of churn happens when a customer intentionally and consciously decides to leave a certain business or terminate their subscription. This is the primary focus area for businesses. Some common reasons for a voluntary churn are:
- Expectations not met by the product or service.
- Unsatisfactory experience with a product or service leads to a search for alternatives.
- An attractive and lucrative offer by a competitor.
- Customers no longer require the service.
To avoid and minimize a voluntary churn, it is important to understand customer expectations and satisfaction with the products or services on offer. A sure-shot solution to this is to provide valuable services which are indispensable and the customers can’t do without them.
Involuntary churn
This kind of churn happens mostly in cases of subscriptions when a business discontinues the service due to non-payment of scheduled charges. Some common reasons leading to non-payment could be:
- Expired card
- Payment declined in case of a lost or stolen card
- Payment declined due to the credit card limit maxed out
- Network issues
Involuntary churn can be avoided by businesses by keeping their checkout pages optimized and implementing smart payment strategies to effectively communicate with customers for payment recovery.
How to calculate churn rate
There are various types of churn rate calculations that businesses need to be aware of to understand different factors influencing the churn dynamics and focus on strategies to be undertaken to overcome high churn rates. Let’s look at a few of the calculations below:
Customer churn rate
This shows the percentage of customers leaving the services.

Revenue churn rate
This is the rate at which revenue is being lost due to subscription cancellations.

Gross revenue churn rate
It is the revenue lost due to cancelled and downgraded subscriptions.

Net revenue churn rate
It is the difference between the (sum of the revenue lost due to cancellations and downgrades) and (the revenue gained from subscription upgrades and reactivations).

Pros and cons of churn rate
Benefits
- Provides transparency about the quality of the business
- Indicates customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction
- Provides competitor comparison to assess acceptable churn
- Ease of calculation
Limitations
- Provides no clarity about the type of customers leaving – old vs new
- Provides no differentiation based on business size: start-up, developing, or maturing
Importance of tracking churn rate
Tracking the churn rate metric is crucial and essential for any business for the following reasons –
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the marketing efforts
- Gauge customer satisfaction
- Implement improvement tactics based on problem points
- Keep tabs on the competition and be ready with a strategy to retain customers
Top reasons for churn and solutions to them:
Understanding the top reasons for customer churn and how to adopt an approach to keep customers around is important for keeping any business profitable and sustainable. Below are some of the common reasons and solutions for them:
#1: Bad product-market fit
This means the wrong customer category is being tapped/attracted by companies. As soon as a customer realizes about the product not being a great fit, it’s less likely for them to stay, upgrade or spread the word.
Solution
Asking questions to understand the needs of a prospective customer will give a clear picture of their expectation. This helps businesses to come up with a marketing copy that targets the right customers resulting in a win-win situation.
#2: Customers dissatisfied with the outcome
The primary reason a customer signs up for a product or service is a specific outcome for their business. The product is merely a tool with features to achieve the outcome. Frustration and disengagement happen when the user does not understand how to put the available features to the best use. This is when they decide to leave even before giving a full trial to the service/product.
Solution
To help customers to get comfortable with the product or services, the below tips should be implemented:
- Provide a well-tested and evaluated onboarding process
- Self-help guides to make the customer understand what features will be helpful and where to find them.
For example, Slack uses tooltips to direct users to key features to reduce the learning curve.

#3: Poor customer service
Even the most knowledgable customers can run into problems from time to time which can quickly turn into big problems if the business is hampered. When such issues arise, no customer wants to browse through a huge knowledge base or chat with bots. They look for real people to solve their problems. In such cases, poor or negligible customer service can lead to high disruptions.
Solution
Prioritizing good customer support right from the beginning can differentiate between brands and help retain customers. Some of the options to do so are:
- Live support
- Offering tiered support levels with different turnaround times based on how much customers are ready to pay
- Providing a comprehensive self-help knowledge base
For example, Wistia replaced their support phone with a chat widget on the website and documentation. Visitors can ask questions when it is online, or leave messages in the support inbox when offline.
#4: Higher trust in competitor product/service
The only important person for the business for whom they want the best is the customer.
A business may have the best-designed product/service, but if the customer thinks the competitor’s product best meets their requirements (price, value, service), that is reason enough for them to leave.
Solution
The below points play a huge role in customer retention:
- Effective pricing: Optimize pricing for the value being provided or expected.
- Match prices to the customers’ willingness to pay.
- Ensure that the customers view the product as an essential part of their business.
- Emphasize the business’s unique selling point in the marketing tactics to attract loyal and long-lasting customers.
#5: Buggy product
Customers lose productivity and revenue if the product they are using develops bugs, glitches, or downtime. This can cause distrust among customers and can become a reason for them to look for other options and leave.
Solution
Communication is the key to maintaining customer trust. Some good practices are:
- Keeping customers in the loop with regular updates
- Keeping a cure to resolve any technical glitch ready during the development phase.
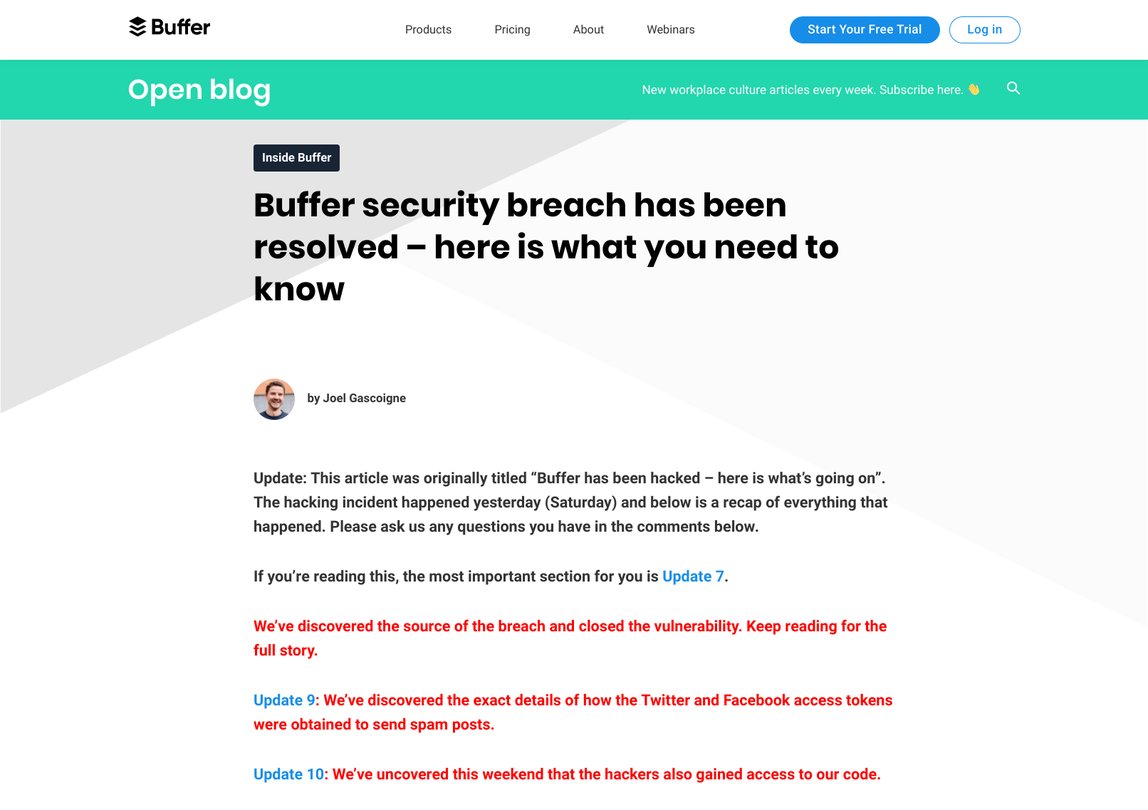
For example, when Buffer was hacked in 2013, they quickly released a blog post and email to update customers about the hack and the progress of the investigation and fix.
Retaining customers is as important as acquiring new ones. Monitoring churn is important for all businesses irrespective of the sector or the type of customers they serve.
Different types of businesses will have different churn rates and as the company grows, the churn rate benchmarks also change. Hence, it is essential to calculate and closely monitor the company churn to make sure it’s under control so that the business thrives under any circumstances.