How to Upsell and Cross-Sell? Strategies to Boost Revenue for eCommerce Businesses
“Buy me those chocolates.”
The kid said sternly, pointing his stubby finger at a big jar of sweets on the shop counter as they waited to check out.
The counter guy grinned. The mother winced.
Download Free: A/B Testing Guide
She just got cross-sold.
Amazon has reported that the business of cross-selling and upselling make up as much as 35% of its revenue.
Product recommendations are responsible for an average of 10-30% of eCommerce site revenues. There’s no reason why upselling and cross-selling shouldn’t work for you. What works between the two is something you can figure out with our powerful A/B testing tool.
In this post, we look at:
- What is upselling and cross-selling?
- Advantages and disadvantages of upselling
- Should you upsell or cross-sell?
- How to improve cross-selling and upselling?
- How to effectively cross-sell and upsell?
- Upselling and cross-selling examples
What are upselling and cross-selling?
Upselling and cross-selling are cousins of selling.
Here’s a fun example that brings out the difference between upselling and cross-selling clearly:
Buy a cow from me, and I’ll offer you a better one for 50 bucks more: the better cow is an upsell.
Buy a cow from me, and I’ll throw in a hay bale for 5 bucks: the hay bale is a cross-sell.
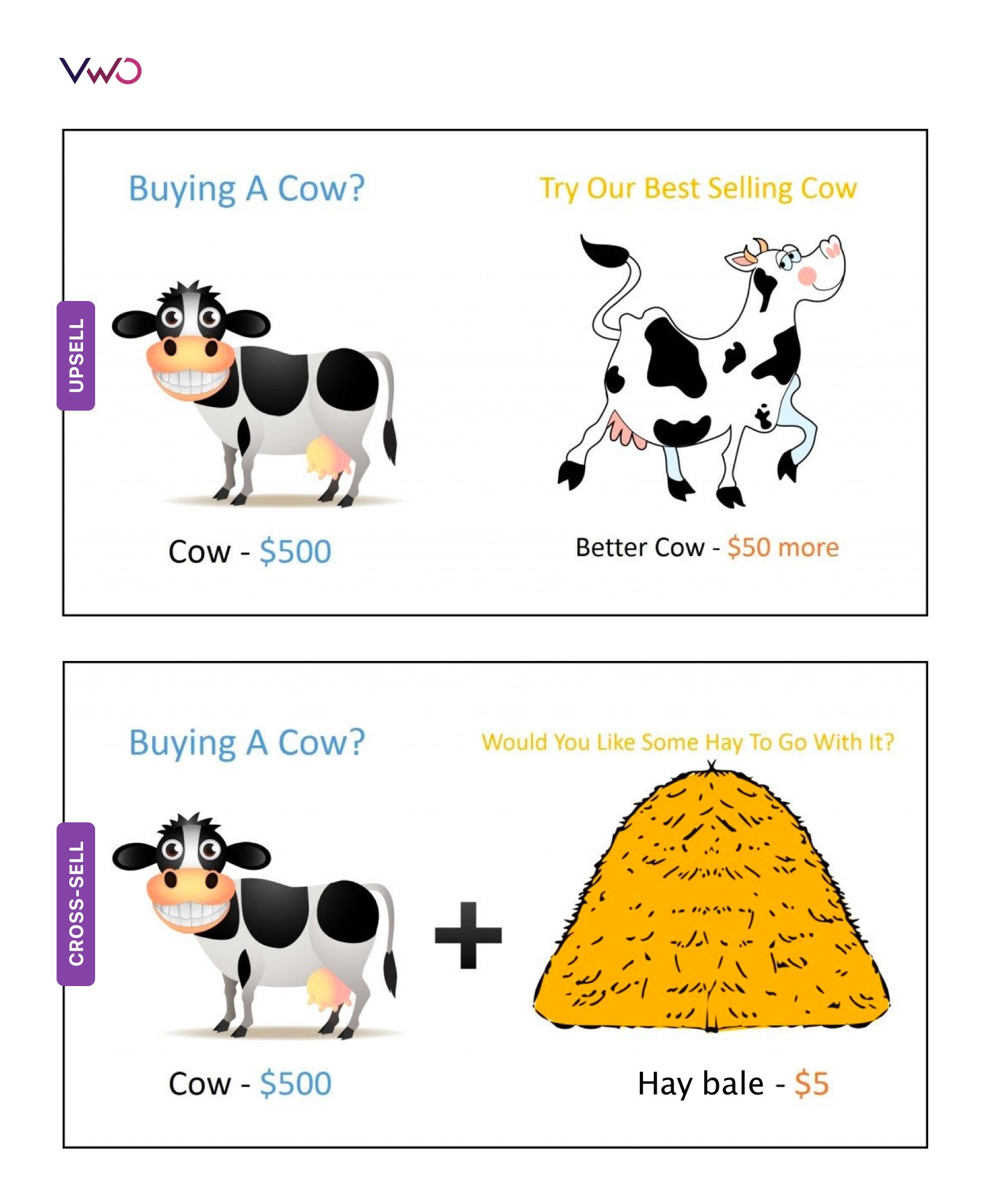
Upselling is a strategy to sell a premium, more expensive version of a product that the customer already owns (or is buying). A premium version is:
- a higher, better model of the product or
- same product with value-add features that raise the perceived value of the offering
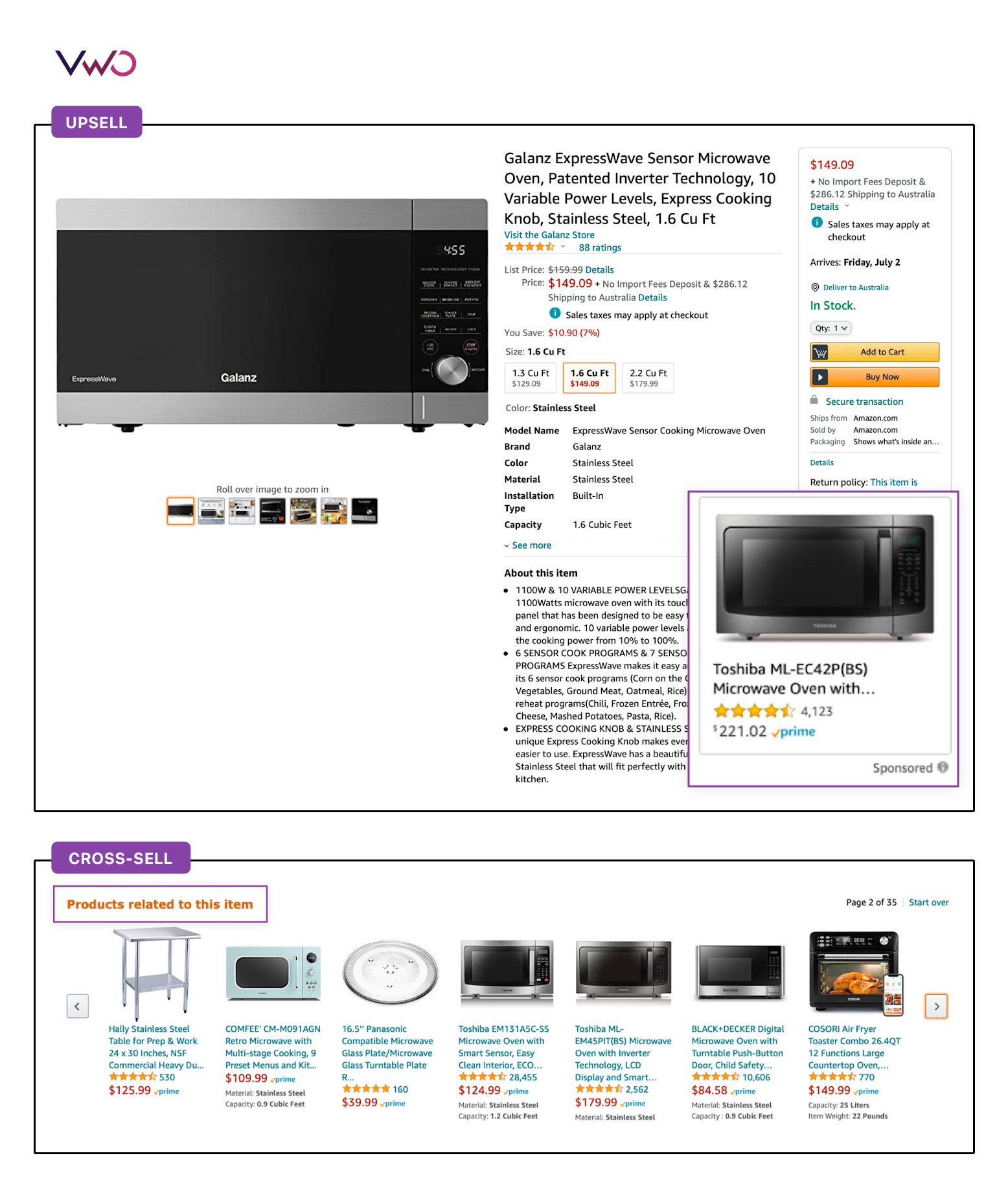
Upselling is the reason why we have a 54” television instead of the 48” we planned for. It’s also the reason you might have subscriptions that include services you don’t use.
Cross-selling is a strategy to sell complementary products, related to the one a customer already owns (or is buying). Such products generally belong to different product categories but will be complementary, like socks with a pair of shoes, or an email marketing tool with CRM software in a B2B cross-selling.
Cross-selling is a battle-ready strategy. Here’s how McDonald’s does it: Their apple pie dispensers are kept right behind the cashier, in full view of customers. The head of the U.S. division for McDonald’s Corp., Jeff Stratton, said in an interview that moving the dispensers to the back kitchen area would probably cut apple pie orders by half.
There is another popular sales technique known as bundling. Bundling is the offspring of cross-selling and upselling. You bundle together the main product and other auxiliary products for a higher price than what the single products are sold for alone.
What is bundling in eCommerce?
By bundling together the camera and two very related (even essential) products, Nikon makes a compelling offer.

Bundling is also quite often used along with a discount to increase the perceived value of the offering.
Pure Bundling is when products are made available only in bundles and cannot be bought individually. Mixed bundling is when both options (individual buy and bundle buy) are made available.
Vineet Kumar from HBS and Timothy Derdenger at Carnegie Mellon University teamed up together and studied bundling as used by Nintendo in their video game market. Revenues fell almost 20% when Nintendo switched from mixed bundling to pure bundling. In the gaming market, prices fall each day, so customers looking to buy just that one thing will choose to wait until it becomes available, likely at a cheaper price.
So should you use upselling, cross-selling, pure bundling, or mixed bundling?
A/B test and find out what works for you!

Specifying a minimum order amount to qualify for free shipping is a great way to use bundling – but it’s important to choose the right minimum order amount that maximizes conversion rates to the bundle.
Amazon does all of this brilliantly.
Benefits of cross-selling and upselling
Cross-selling and upselling are often (and mistakenly) seen as unethical practices to squeeze more sales out of the customer.
As a marketing strategy, however, cross-selling and upselling should be used to ‘help customers win’. It’s about making recommendations that might better meet a customer’s current needs and aiding them to make a choice by being fully informed about their options.
Remind Bob to buy some batteries along with his new wall clock
Jack might be looking for something more powerful than an i5 processor, show him the i7, too.
So how do cross-selling and upselling help you as a marketer?
Increases customer retention
Leaving aside impulse buys, customers buy products and services to solve a problem. They are aware of the problem, but might not be aware of the best solution to the problem.
Steve Jobs was right when he said ‘People don’t know what they want until you show it to them.’ Upselling or cross-selling done right helps the customer find more value than they were expecting. It can increase revenues by up to 43%, thereby improving your customer retention and repeat purchases.
Increases average order value and lifetime value
Cross-selling and upselling increase your overall order value and average order value, creating revenue and profit at a very low incremental cost. You’ve already spent valuable marketing dollars to get the customer to your eCommerce store, so maximizing order value is key to ROI.
A Marketing Metric study reports that the probability of selling to an existing customer is 60-70%. The probability of selling to a new prospect is 5-20%. Upselling to existing customers is a great strategy to boost lifetime value.
Lowered customer acquisition cost
Upselling and cross-selling strategies offer a great advantage. As you sell products in bundles and push for upgrades for a high-intent lead, you get more out of a single campaign instead of running a separate campaign for an individual product or an upgrade. Thus, it helps to reduce the cost of acquiring new customers.
Businesses can optimize their marketing efforts with upsell and cross-sell, reaching a larger audience and getting the most out of each customer interaction. This approach saves resources and eliminates the need for separate campaigns for different products or upgrades, resulting in significant cost savings.
If you wish to learn more about motivating your visitors to make a purchase decision, listen to our insightful talk with Mogens Møller on the VWO Podcast.
Disadvantages of cross-selling and upselling
Cross-selling and upselling are common strategies used by many companies. However, if not carefully implemented, these strategies lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Two major drawbacks can come with imperfectly implemented cross-sell and upsell techniques.
Decision overload
If cross-selling involves presenting an overwhelming number of product combinations and choices to customers, it can result in decision overload. When customers see too many options, they may feel overwhelmed and find it difficult to make a decision. This can lead to frustration and, in some cases, customers may abandon the purchase altogether or simply opt for the originally chosen product without considering any additional offerings.
Simplifying the cross-selling process and offering targeted and relevant choices can help alleviate decision overload and improve the likelihood of successful cross-selling opportunities.
Likewise, complex pricing plans with unclear communication related to benefits can churn customers during upselling as they can’t understand the advantage that the upsell will bring.
Sales-focused user experience
Overly aggressive or intrusive upselling and cross-selling efforts have the potential to annoy and frustrate customers. Continuously bombarding them with excessive offers or pushing unrelated products can create a negative perception, undermining their overall experience.
Customers appreciate a seamless and personalized journey, and when they feel inundated with relentless sales pitches, it can detract from their enjoyment and diminish their trust in the brand.
Download Free: A/B Testing Guide
Should you upsell or cross-sell in eCommerce?
There’s no easy answer as to whether upsell or cross-sell is the best strategy. The best way to decide is through A/B testing.
Let’s understand it through a hypothetical scenario for an eCommerce store specializing in electronic gadgets and accessories. The marketing team at the store identified an audience segment aged 25-34 who were highly engaged with their website but had a low average order value.
The marketing team came up with two hypotheses related to cross-selling and upselling to increase average order value and wanted to A/B test using VWO.
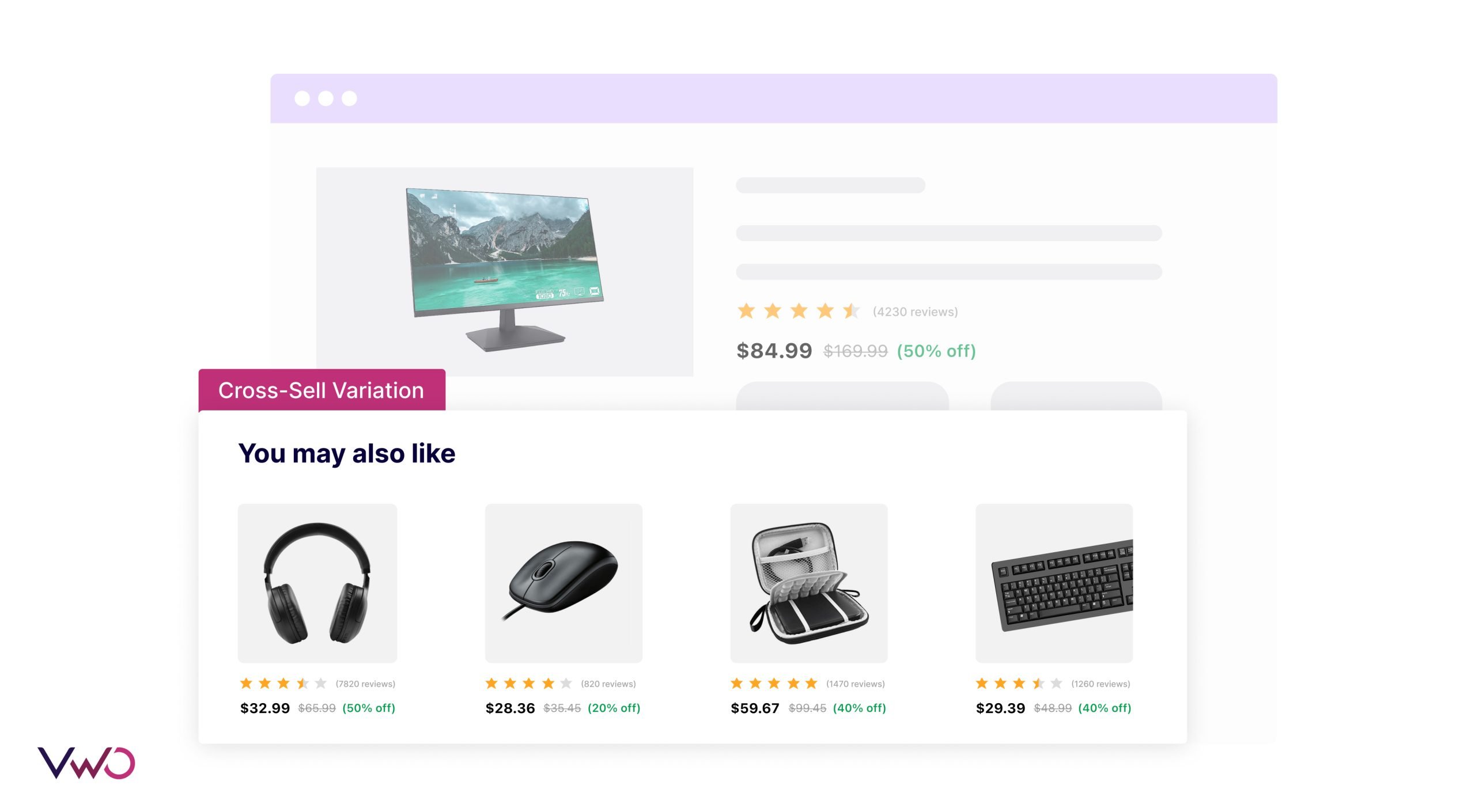
For the cross-sell variation, the team added a personalized “You May Also Like” section below the main product being viewed. They curated a list of complementary accessories, such as wireless headphones and protective cases, alongside the primary product.
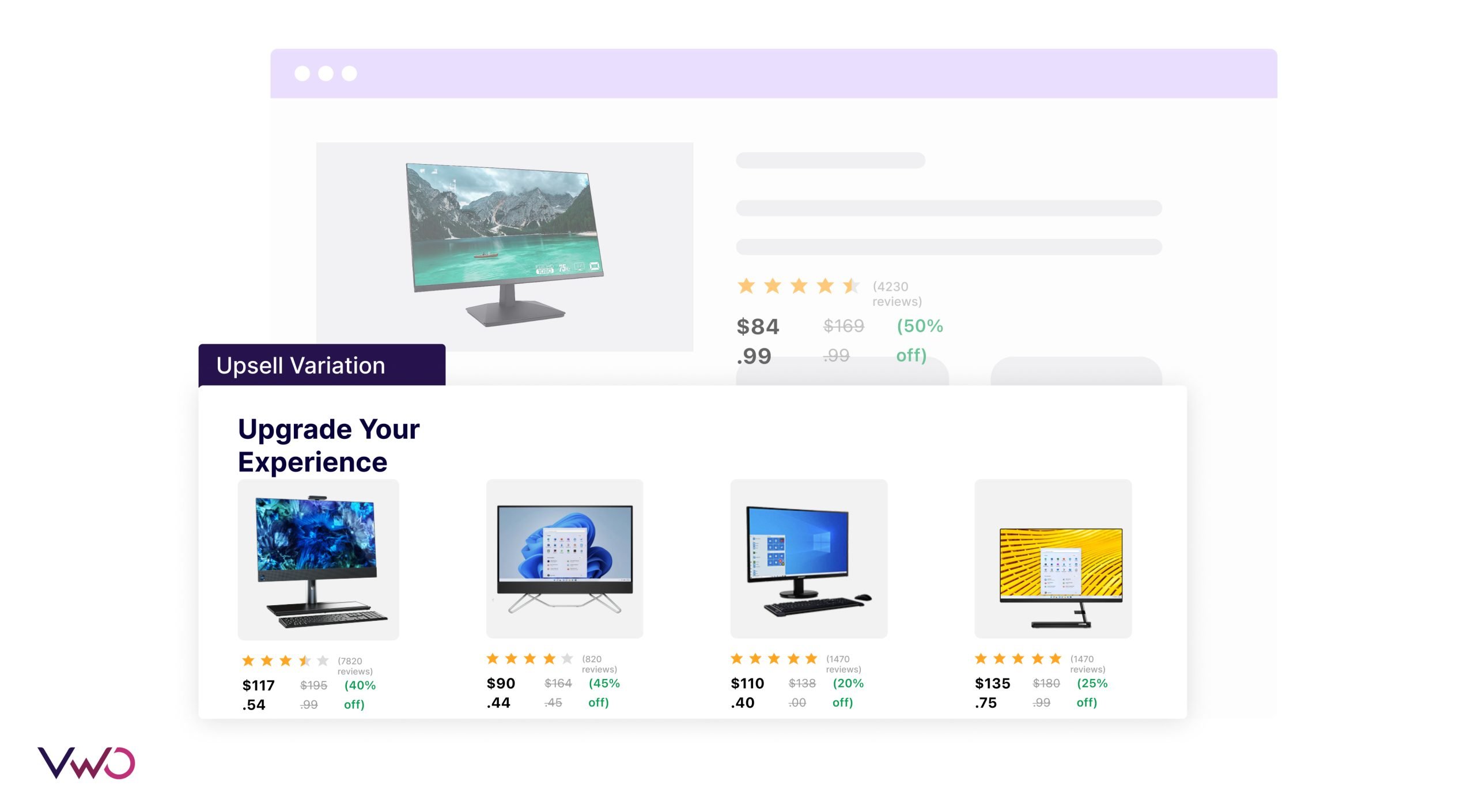
For the upsell variation, the team introduced an “Upgrade Your Experience” section on the product page. They showcase premium versions or higher-end models of the product being viewed, highlighting the enhanced features, durability, or performance advantages.
The marketing team ran the A/B test for 14 days and monitored the average order value and revenue. The test ended with the upsell variation yielding a higher average order value of $110 and revenue of $28000 compared to the cross-sell variation at $90 and revenue of $25000, indicating that customers who were exposed to the upsell section were more likely to opt for higher-priced products.
Based on the test, the marketing team at the eCommerce store will prioritize the upsell approach as it resulted in both a higher average order value and revenue.
That’s why it’s important to go for an A/B test as it will prioritize either cross-sell or upsell based on the version with better conversion rate, profit margins, and customer feedback.
Understand why VWO is the best A/B testing tool in the market
PRWD head of usability, Paul Rouke explains why cross-sell works best on checkout pages.

How to improve cross-selling and upselling?
One of the most common ways to upsell is to suggest the next higher model. But when it’s just 4% that you are targeting, the margin for error is as thin as the edge of a blade.
Here are some suggestions to improve upsell:
- Promote your most reviewed or most sold products
- Give more prominent space for the upsell, display testimonials for the upsell
- If you have customer personas in place, use those to make relevant suggestions
- Make suggestions relevant by giving context: why should I buy that instead of this?
And always, always, make sure you suggest products from the same category. Don’t ask your website visitor to buy a 17-inch laptop when they’re shopping for a MacBook Air. The two products don’t satisfy the same needs.
Use cross-sell techniques more on the check-out page to tap into impulse buying:
- Cross-sell products should be at least 60% cheaper than the product added to the cart so buyers consider adding it to their carts even though they didn’t originally intend to purchase them
- Go for products that are easily missed out: filters for lenses, earphones for mobile phones, lighter for a gas stove, and of course, scrub for cows.. the possibilities are endless
- Try not to bombard them with too many choices that distract them, so they end up abandoning their cart.
If you are manually pushing upsell/cross-sell suggestions, it would be worthwhile to automate the system. Products should be categorized and related products should be tagged so as to enable automation.
How to effectively cross-sell and upsell?
Upsell and cross-sell works when you are able to ease the decision making process of a customer.
A study by Bain showed that reducing complexity and narrowing choices can boost revenues by 5-40% and cut costs by 10-35%.
1. Upsell smart by narrowing choices
Too many choices can be paralyzing. Professor Iyengar and her research assistants conducted a study on the effect of choices in the California Gourmet market. They set up booths of Wilkin and Sons Jams — one offered an assortment of 24 jams while the other had on display 6 jam varieties.
60% of the visitors stopped by the larger booth while only 40% flocked to the one with fewer choices.
But 30% of visitors that sampled at the small booth made a buy, while only 3% of the 60% visitors to the larger booth went on to make a purchase.
Don’t bombard your current customers with too many choices. If they’ve already said no to an upsell product, do not push for it. Think of upselling as a gentle suggestion, not an aggressive sales tactic. And when in doubt, A/B test!

2. Offer bundles to reduce decision complexity
Every action the user has to take makes the decision making more complex. Think of ways to reduce the number of actions in a buying decision. We have a limited amount of energy to be spent on decision making.
Bundling brings together related products that are of relevance to a customer. Buying them individually involves more decision making and more steps. Whereas through bundling, in one a customer is able to buy multiple products together.
It’s also important to understand how we make decisions. Exactly how rational are we at decision making?
3. Use price anchoring: The surprising power of dummy choices
A few years back, The Economist ran an ad that looked like this:

You get a web-only subscription for $59, a print-only subscription for $125 or both, again, for $125! Needless to say, the print-only subscription option is a dummy choice. Who would ever choose an inferior option when the price is the same?
Dan Ariely took the ad and took it to 100 MIT students to see what they would choose.

An overwhelming majority chose what seemed the ‘best’ option – both print and web subscription at $125.
16% chose the web-only subscription. Nobody chose the print-only subscription at $125.
Dan then took off the middle choice—the print-only one. And ran the test again on 100 people. This is how the opt-in rates looked now.

Surprisingly, the majority (68%) people chose the cheaper option when the dummy choice was removed. The print and web subscription that saw 84% subscription in the presence of the dummy choice now got a significantly low 32% subscription rate.
An inferior choice makes a similar but superior choice look better even when other options are cheaper.
Actionable Tip: consider a customer looking at a top-tier entry-level DSLR. Show him a mid-level DSLR without add-ons for a marginally higher price and the same mid-level DSLR with add-ons at the same higher price.
Upsell it with the proper communication — how does the mid-level DSLR help the customer win? — and you have a good probability of making the upsell.
4. Be helpful and offer value, not pushy or aggressive
A key principle in cross-selling and upselling is to assist the customer, suggesting products that make sense to them and are relevant to their needs. Use data and customer behaviors to offer relevant products that are likely to meet their needs or solve a current or potential problem.
Here’s what you shouldn’t do:
- Suggest upsells and cross-sells before a customer picks a product
- Bombard customers with too many cross-sell and upsell products
- Sly tactics like hiding pre-selected add-ons in the hope customers don’t notice it
5. Don’t forget post-purchase cross-selling
Your opportunity to cross-sell doesn’t end once the customer has checked out. In fact, the experience after the initial purchase is a key moment in the customer journey that too many eCommerce businesses forget about. Don’t just send the receipt and the product – use the opportunity to develop loyalty and make special offers after customer purchases.
Use emails, confirmation pages, and other post-purchase communications to offer further products, incentives, and value to the customer.
6. Personalize customer experience
Personalizing products or offering recommendations for an upsell or cross-sell campaign based on past behavior, purchases, and geography creates a more tailored and relevant customer experience, increasing the likelihood that customers will find value in the additional offerings presented to them.
For example, a SaaS company can create an upsell opportunity for its paid customers by analyzing their past behavior and offering an upgrade plan with new features that will address their pain points.
Personalization enables a business to provide customized solutions to their users’ needs resulting in improved customer satisfaction and business outcomes.
Did you know? VWO helps you create 1000s of unique personalization journeys
Upselling and cross-selling examples
Here are two real-world examples of upselling and cross-selling, illustrating how these brands leveraged these strategies to their advantage while employing the techniques we discussed earlier.
1. Overstock
Overstock, a home goods internet retailer, is an excellent example of cross-selling. Below is the product landing page where you can see a ‘frequently bought together’ section.
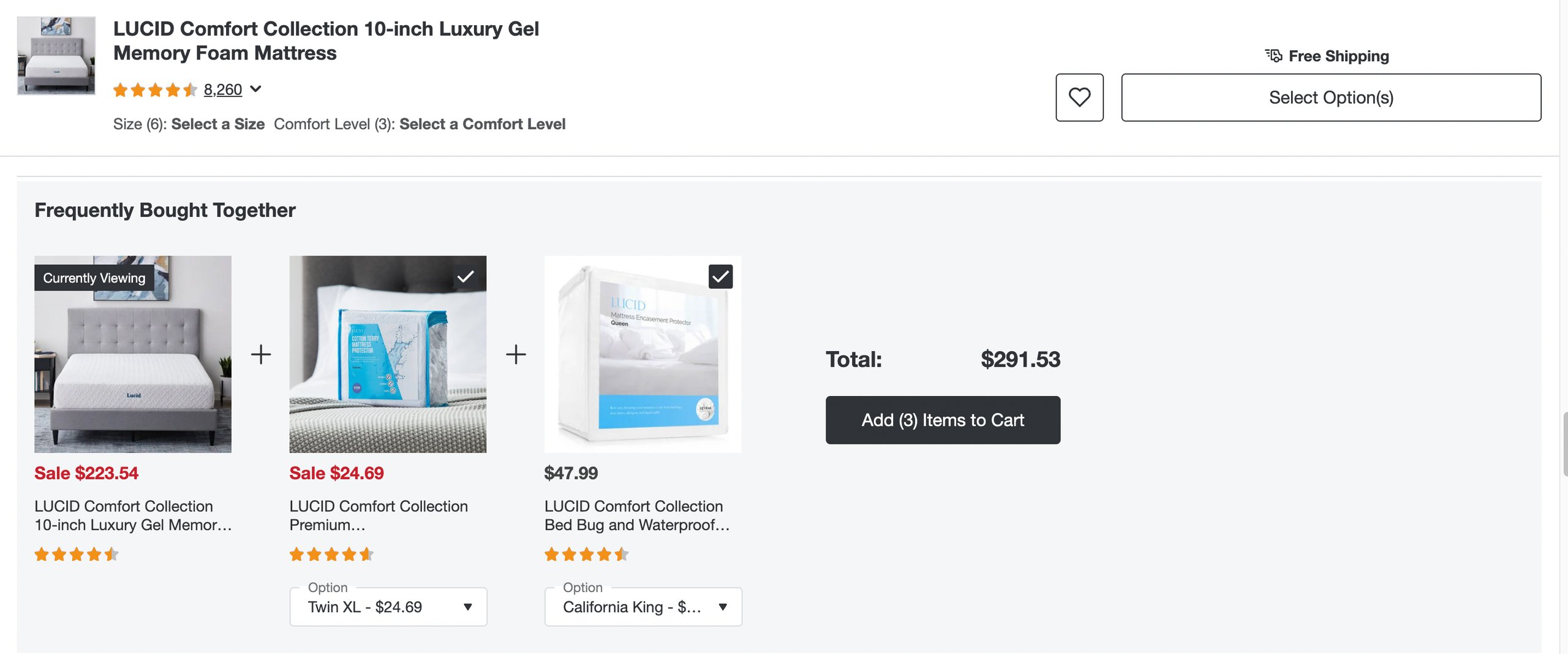
The section is designed to suggest related products that customers may find useful, along with the main product they are considering. The section comes as natural and is not intrusive to the user experience.
Overstock allows customers to select or deselect related products, which enables customers to customize their purchase and choose only the additional items they are interested in rather than being forced to buy the entire bundle. It enhances the chances of customers adding more items to their cart with cross-selling techniques, resulting in increased sales.
2. Semrush
Semrush, a SaaS platform for online marketing is a great upselling example. It utilizes a compelling upsell technique by enabling users to create free accounts and gain limited access to platform features. Then, it allows them to assess its potential and become acquainted with it. After providing this limited access, the platform strategically places CTAs on each feature page to encourage customers to upgrade their plans.
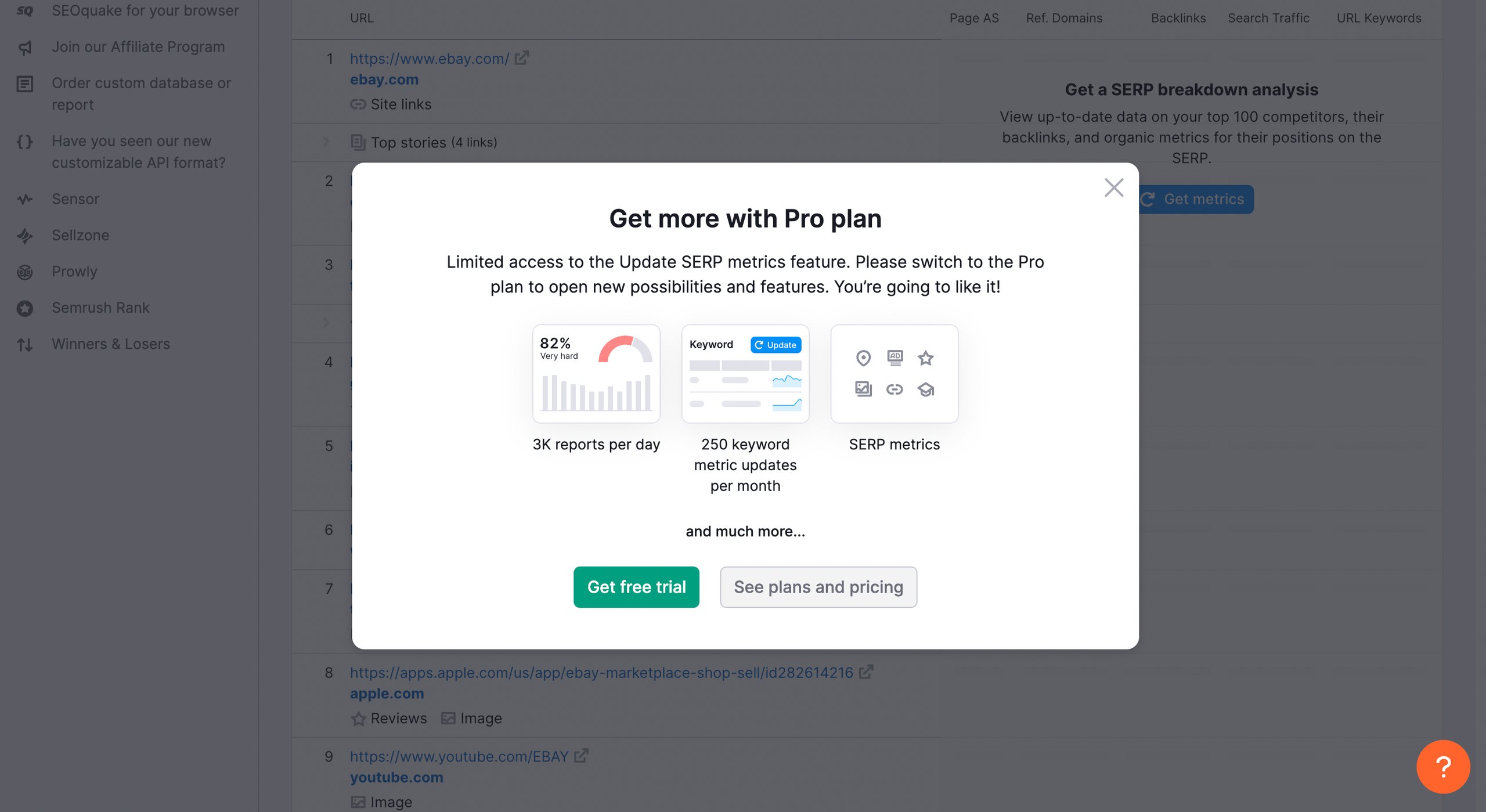
Also, Semrush doesn’t stop once a free plan user upgrades. For paying users, Semrush employs the same upsell technique by utilizing CTAs that prompt them to upgrade to plans offering more advanced features and personalized recommendations.
Thus, it gradually makes users habitual to its Saas platform, then strategically makes upsells that cater to the online marketing needs of the users.
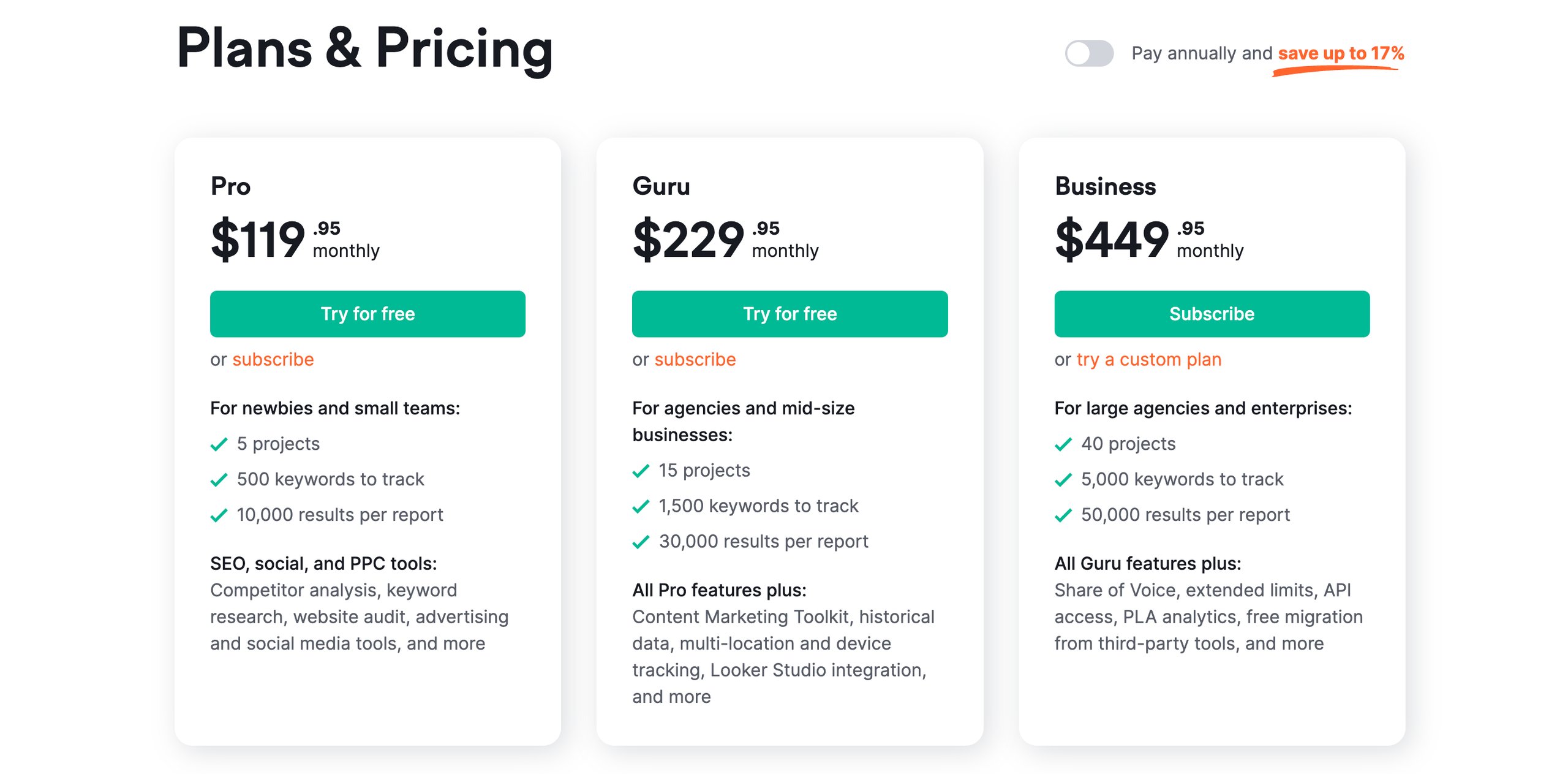
Also, it gives a massively discounted price on yearly plans to entice users to upgrade from monthly to annual subscriptions.
Final takeaways
If there’s one thing to take away from this post, it has to be this:
Upsell and cross-sell techniques are powerful strategies that can help customers make better decisions, faster.
To figure out which of these works for your customers, you shouldn’t rely on guesswork. A/B test differing cross-sell and upsell marketing strategies for your multiple visitor segments to determine what works for each of them, so you can deploy the one that drives maximum improvement in sales.
VWO Testing allows you to create and run tests on your key pages to experiment with the various upsell and cross-sell tactics discussed above and optimize them for increased revenue. With an easy-to-use Visual Editor, you can create and run tests independently without having to rely on your IT team. Sign up for a free trial to assess the tool for yourself or request a personalized demo from one of VWO’s optimization experts.